RTP 2500 Series Compounds
This data provides comparative information on the shielding performance of standard RTP Company PC/ABS alloy compounds using various combinations of additives and loading levels.
Instead of off-the-shelf solutions, RTP Company routinely develops specialty compounds with a precise combination of properties such as conductivity, flame retardance, structural reinforcement, color, and wear resistance to meet your exact application requirements.
RTP 2500 Series
Polycarbonate/ABS Alloy Compounds
PC/ABS alloys process with the ease of ABS (RTP 600 Series) materials yet have a toughness similar to polycarbonate (RTP 300 Series) materials. The high heat distortion of the alloy is an improvement over ABS, while the low temperature impact resistance gives it an advantage over polycarbonate.
By reinforcing the alloy with glass fiber, nickel-coated carbon fiber and/or stainless steel, RTP Company can produce compounds that meet the structural, static dissipative and EMI/RFI shielding requirements of the computer and business machine markets.
RTP Company’s EMI 2580 FR Series PC/ABS compounds incorporate nickel-coated carbon fiber and flame retardant additives. These compounds are UL recognized with a ratings of V-0 @ 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) and 5VA @ 1/8 inch (3.2 mm).
Carbon Fiber Products
- Reinforcing
- Highest strength/modulus properties of the common shielding additives
- Lowest cost of the common shielding additives
- Low shielding performance
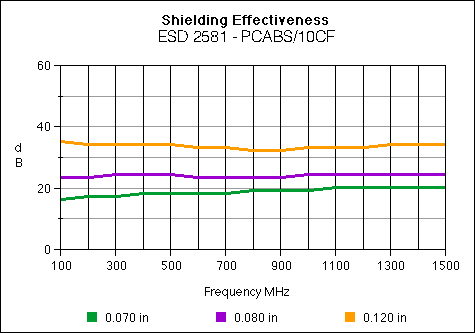
ESD 2581
Carbon Fiber 10%
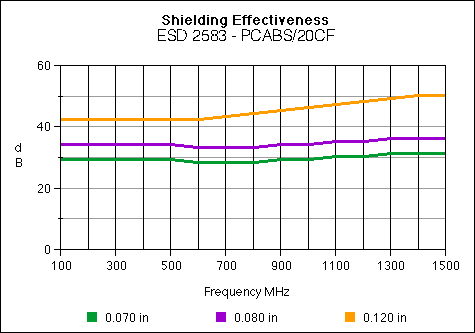
ESD 2583
Carbon Fiber 20%
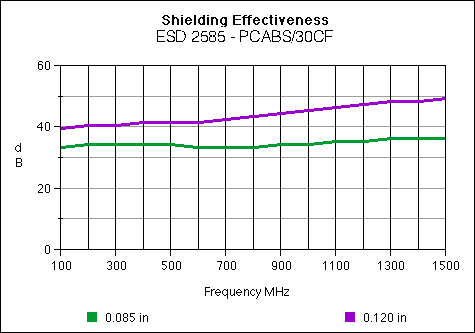
ESD 2585
Carbon Fiber 30%
Stainless Steel Fiber Products
- Non-reinforcing
- Minimal effect on neat resin properties
- Similar mold shrinkage to neat resin
- Good shielding-to-cost performance
- Best colorability of the common shielding additives
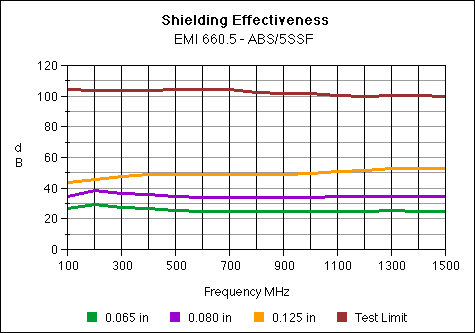
EMI 2560.5
Stainless Steel 5%
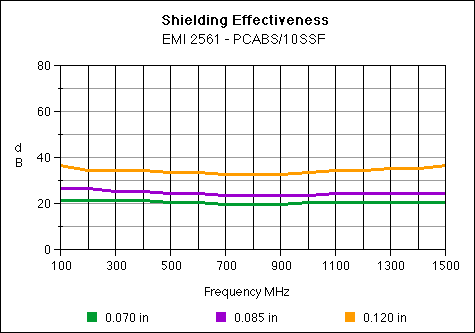
EMI 2561
Stainless Steel 10%
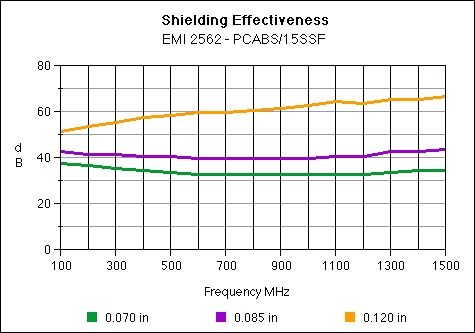
EMI 2562
Stainless Steel 15%
ASTM D4935: Standard Test Method for Measuring the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Planar Materials
This test method provides a procedure for measuring the electromagnetic (EM) shielding effectiveness (SE) of a material due to a plane-wave, far-field EM wave. The test utilizes a coaxial transmission line to determine the shielding effectiveness of a given material. The test method is valid for a frequency range of 30 MHz to 1.5 GHz. Various thicknesses and types of materials can be tested to acquire a relative ranking of shielding effectiveness.
Supporting Product Information
Chemical Resistance
Information on resin resistance to chemical and environmental exposure.
RTP Company Nomenclature
Guide to the identification system used for RTP Company products.
EMI Primer
The nuts and bolts of EMI and how thermoplastics can function as a shield.
No information supplied by RTP Company constitutes a warranty regarding product performance or use. Any information regarding performance or use is only offered as suggestion for investigation for use, based upon RTP Company or other customer experience. RTP Company makes no warranties, expressed or implied, concerning the suitability or fitness of any of its products for any particular purpose. It is the responsibility of the customer to determine that the product is safe, lawful and technically suitable for the intended use. The disclosure of information herein is not a license to operate under, or a recommendation to infringe any patents.




