Wear factor (K) is an indication of a materials resistance to wear as a function of the volume of material lost, force (load) and velocity at the wear interface and time. It is often determined using a “thrust washer” wear testing apparatus per ASTM D3702 in which a molded plastic specimen is rotated against a substrate thrust washer under set pressure and velocity conditions.
A wear factor is calculated with the equation W=K*F*V*T. In this equation W is wear volume (in3), K is wear factor (in3 min/ft lb hr)10-10, F is force (lb), V is velocity (ft/min), and T is elapsed time (hr).
A material with a lower wear factor (K) has greater resistance to wear and these values are useful for material comparison purposes.
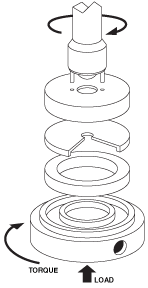
[ View wear data in metric units | Return to wear data resin system list ]
Plastic vs Plastic
| Test Conditions
PV 1000 Load 4 Speed 50 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotating Sample | vs | Stationary Sample | µ Dynamic |
||
| RTP Product | Wear
Factor |
RTP Product | Wear
Factor |
||
|
POM Unfilled |
13 | vs |
PA 6/6 Unfilled |
132 | 0.24 |
|
POM Unfilled |
61 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber |
228 | 0.22 |
|
POM Unfilled |
61 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
106 | 0.25 |
|
POM Unfilled |
13 | vs |
PC Unfilled |
41 | 0.47 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
4 | vs |
PA 6/6 Unfilled |
11 | 0.10 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
40 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber |
149 | 0.24 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
68 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
118 | 0.20 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
6 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Carbon Fiber 15% PTFE |
13 | 0.23 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
48 | vs |
PC Unfilled |
99 | 0.42 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
26 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
63 | 0.27 |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
44 | vs | 88 | 0.42 | |
|
POM 20% PTFE |
8 | vs |
PA 6/6 20% PTFE |
48 | 0.32 |
|
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
4 | vs |
PA 6/6 20% PTFE |
98 | 0.14 |
|
POM 30& Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
222 | vs |
PA 6/6 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
244 | 0.24 |
|
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
93 | vs |
PA 6/12 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
173 | 0.20 |
|
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
433 | vs |
PC 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
626 | 0.28 |
|
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
302 | vs |
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
103 | 0.28 |
|
POM 30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
86 | vs |
PBT 15% Glass Fiber |
218 | 0.23 |
|
POM PTFE Lubricated Silicone Lubricated UL94 HB |
1167 | vs |
POM PTFE Lubricated Silicone Lubricated UL94 HB |
326 | 0.36 |
| RTP 899 X 93812
POM Glass Fiber Reinforced Internally Lubricated |
19 | vs |
POM PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
15 | 0.30 |
| RTP 899 X 93812
POM Glass Fiber Reinforced Internally Lubricated |
37 | vs |
POM Unfilled |
1055 | 0.39 |
|
POM PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
73 | vs |
POM PTFE Lubricated Silicone Lubricated UL94 HB |
127 | 0.23 |
|
POM PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
30 | vs |
POM PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
22 | 0.25 |
|
POM PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
2 | vs |
PA 6/6 20% PTFE |
44 | 0.27 |
- Thrust washer testing conducted per ASTM D 3702
- Wear Factor units: (in3 min/ft lb hr)10-10
- PV units: lb ft/in2 min
- Load units: lbs
- Speed units: ft/min
Plastic vs Steel
| RTP Product | RTP Product Tested vs Steel (1018 C) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Conditions
PV 2000 Load 8 Speed 50 |
Test Conditions
PV 5000 Load 10 Speed 100 |
Test Conditions
PV 10000 Load 40 Speed 50 |
||||
| Wear Factor |
µ Dynamic |
Wear Factor |
µ Dynamic |
Wear Factor |
µ Dynamic |
|
|
Unfilled POM |
93 | 0.40 | 102 | 0.42 | 150 | 0.44 |
|
2% Silicone |
42 | 0.43 | 46 | 0.41 | 60 | 0.51 |
|
10% PTFE |
85 | 0.68 | 13 | 0.29 | 7 | 0.18 |
|
15% PTFE |
67 | 0.26 | 22 | 0.34 | ||
|
20% PTFE |
82 | 0.25 | 14 | 0.34 | ||
|
10% PTFE 2% Silicone |
9 | 0.29 | 6 | 0.24 | 9 | 0.14 |
|
30% Glass Fiber 15% PTFE |
71 | 0.46 | 135 | 0.36 | 867 | 0.34 |
|
15% Carbon Fiber 10% PTFE |
160 | 0.30 | 219 | 0.40 | ||
|
10% Aramid Fiber 15% PTFE |
23 | 0.18 | 8 | 0.25 | 3 | 0.19 |
|
PFPE Lubricated PTFE Lubricated |
14 | 0.44 | 43 | 0.37 | 78 | 0.46 |
- Thrust washer testing conducted per ASTM D 3702
- Wear Factor units: (in3 min/ft lb hr)10-10
- PV units: lb ft/in2 min
- Load units: lbs
- Speed units: ft/min
Comparing competitive data note
RTP Company reports Wear Factors per unit Force (KF) with units of (in3 min/ft lb hr)10-10. This is the industry standard way to calculate and report Wear Factor. Some suppliers report Wear Factors per unit Pressure (KP) with units of (in5 min/ft lb hr)10-10. This value is arrived at by dividing the KF by the contact surface of the test specimen (0.35 in2). As result of this reporting discrepency, RTP Company’s Wear Factor values appear to be significantly higher. For example a KP of 3 (in5 min/ft lb hr)10-10 would be equal to KF of 3/0.35 = 8.57 (in3 min/ft lb hr)10-10.
No information supplied by RTP Company constitutes a warranty regarding product performance or use. Any information regarding performance or use is only offered as suggestion for investigation for use, based upon RTP Company or other customer experience. RTP Company makes no warranties, expressed or implied, concerning the suitability or fitness of any of its products for any particular purpose. It is the responsibility of the customer to determine that the product is safe, lawful and technically suitable for the intended use. The disclosure of information herein is not a license to operate under, or a recommendation to infringe any patents.




